Exploring the differences between Private Health Cover and Public Healthcare opens up a world of contrasting systems and services. This informative discussion aims to shed light on the intricacies of healthcare funding, coverage, and accessibility, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Delving into the realms of cost, coverage, and regulatory frameworks, this analysis aims to equip individuals with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions regarding their healthcare options.
Understanding Private Health Cover and Public Healthcare
Private health cover refers to health insurance plans provided by private companies, where individuals pay premiums to access healthcare services. On the other hand, public healthcare is funded and administered by the government, providing healthcare services to all citizens regardless of their ability to pay.
Differences in Funding, Administration, and Coverage
Private health cover is funded through individual premiums, employer contributions, and out-of-pocket payments. The administration is handled by private insurance companies, and coverage varies based on the plan purchased, often including services like dental and vision care.In contrast, public healthcare is funded through taxes collected by the government.
The administration is overseen by government agencies, and coverage is universal, providing essential medical services to all citizens. This system aims to ensure equal access to healthcare for everyone, regardless of income or employment status.
Examples of Countries with Predominantly Private Health Cover vs Public Healthcare Systems
Countries like the United States, Switzerland, and Germany have predominantly private health cover systems, where individuals are responsible for obtaining their insurance and healthcare services through private companies.On the other hand, countries like Canada, the United Kingdom, and Australia have public healthcare systems, where the government is the primary provider of healthcare services to the population.
Citizens in these countries typically have access to essential medical care through publicly funded programs like Medicare and the National Health Service.
Cost Comparison
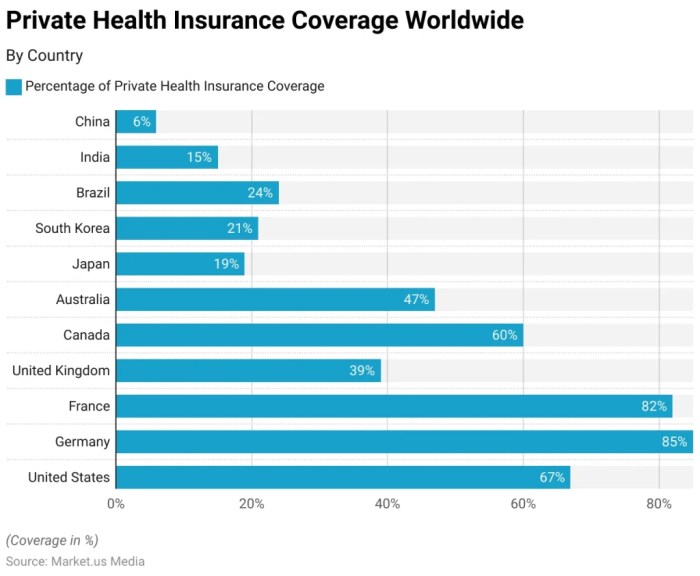
Private health cover typically involves various costs, including premiums, out-of-pocket expenses, and deductibles. Premiums are regular payments made to the insurance provider to maintain coverage. Out-of-pocket expenses are costs incurred by the individual for healthcare services not fully covered by the insurance plan.
Deductibles refer to the amount the insured person must pay before the insurance provider begins to cover costs.
Private Health Cover Costs
- Premiums: Monthly or annual payments to maintain coverage.
- Out-of-pocket expenses: Costs not covered by the insurance plan, such as co-pays or non-network provider charges.
- Deductibles: Amount the insured individual must pay before the insurance provider covers costs.
Public Healthcare Funding
In contrast, public healthcare systems are funded through various means, including taxes. Taxpayers contribute to the funding of public healthcare services, which are then provided to all residents regardless of their ability to pay. This funding model aims to ensure universal access to essential healthcare services for the population.
Affordability Comparison
- Private Health Cover: Generally more expensive due to premiums, out-of-pocket expenses, and deductibles, but offers more choice and potentially shorter wait times for certain services.
- Public Healthcare: Funded through taxes, making it more affordable for individuals and families with lower incomes. However, it may involve longer wait times for non-emergency procedures.
Coverage and Services
Private health insurance plans typically cover a wide range of services beyond what public healthcare systems offer. These services often include elective procedures, dental care, vision care, and alternative therapies that may not be covered by public healthcare.
Private Health Insurance Services
- Elective procedures such as cosmetic surgery and fertility treatments
- Dental care including routine check-ups, cleanings, and orthodontics
- Vision care such as eye exams, glasses, and contact lenses
- Alternative therapies like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and naturopathy
Public Healthcare Services
Public healthcare systems typically provide essential medical services to all residents regardless of their insurance coverage. These services may include emergency care, hospitalizations, primary care visits, and preventive screenings.
Quality of Care, Waiting Times, and Access to Specialists
In terms of quality of care, private healthcare often offers more personalized attention and shorter wait times for appointments and procedures compared to public healthcare. Private insurance plans also grant easier access to specialist doctors and advanced treatments, providing a higher level of care overall.
Accessibility and Availability
In terms of accessing healthcare services, both private health cover and public healthcare have their own set of criteria and limitations. Let’s delve into the specifics to understand how they impact the overall accessibility and availability of healthcare.
Eligibility Criteria for Private Health Cover
Private health cover often comes with eligibility criteria that individuals need to meet in order to enroll in a plan. These criteria can vary depending on the insurance provider and the type of coverage desired. Factors such as age, pre-existing conditions, and lifestyle habits may influence eligibility.
Additionally, certain treatments or services may be excluded from coverage, leading to limitations in accessibility for some individuals.
Exclusions in Private Health Cover
Private health cover may exclude certain treatments, procedures, or services from coverage. These exclusions can impact the accessibility of healthcare for individuals who require those specific treatments. It’s important for individuals to carefully review the inclusions and exclusions of their chosen plan to ensure they have access to the necessary healthcare services when needed.
Availability of Healthcare Services in Public Systems
Public healthcare systems aim to provide universal access to essential healthcare services for all residents. However, the availability of these services can be influenced by factors such as wait times and geographical coverage. Longer wait times for non-emergency procedures or specialist appointments can affect accessibility to timely healthcare.
Moreover, individuals living in remote or underserved areas may face challenges in accessing certain healthcare services due to limited geographical coverage.
Impact of Choice on Overall Accessibility
The choice between private health cover and public healthcare can significantly impact overall accessibility to healthcare services. While private health cover may offer faster access to certain treatments and services, it comes with eligibility criteria and potential exclusions that could limit accessibility for some individuals.
On the other hand, public healthcare systems strive to provide universal access to essential services, but factors like wait times and geographical limitations can affect the availability of care. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
Regulatory Differences
In examining the regulatory framework governing private health cover and public healthcare, it is essential to understand the differences in government oversight, regulations, and compliance requirements for both systems. Additionally, exploring the roles of insurance companies, healthcare providers, and government agencies in each system can provide valuable insights into how healthcare is managed and delivered.
Government Oversight and Regulations
- Private Health Cover: Private health cover is regulated by government bodies to ensure that insurance companies adhere to certain standards and guidelines. These regulations may vary depending on the country or region, but generally aim to protect consumers and maintain the integrity of the healthcare system.
- Public Healthcare: Public healthcare is typically overseen by government agencies responsible for funding, managing, and delivering healthcare services to the general population. These agencies set regulations and guidelines for healthcare providers to follow in order to maintain quality and accessibility of care.
Compliance Requirements
- Private Health Cover: Insurance companies offering private health cover must comply with regulations related to pricing, coverage, and customer service. These requirements are designed to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in the private healthcare sector.
- Public Healthcare: Healthcare providers in the public sector are required to comply with government standards regarding quality of care, patient safety, and cost-effectiveness. Compliance requirements help maintain consistency and effectiveness in public healthcare delivery.
Roles of Stakeholders
- Private Health Cover: Insurance companies play a significant role in private health cover by offering insurance plans, managing claims, and negotiating with healthcare providers. They work closely with government agencies to ensure compliance and consumer protection.
- Public Healthcare: Government agencies oversee the funding, administration, and regulation of public healthcare services. Healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and practitioners, deliver care to patients based on government guidelines and funding allocations.
Last Point
In conclusion, the comparison between Private Health Cover and Public Healthcare highlights the nuances of each system, offering valuable insights into the pros and cons of both. As individuals navigate the complex landscape of healthcare, understanding these differences is crucial in making the right choices for themselves and their families.
FAQ Guide
Is private health cover more expensive than public healthcare?
Private health cover can be more expensive due to premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, but it often offers more comprehensive coverage.
What services are typically covered by private health insurance plans?
Private health insurance plans usually cover services like hospital stays, specialist consultations, and certain medical procedures.
How does government oversight differ between private health cover and public healthcare?
Private health cover is regulated by insurance authorities, while public healthcare systems are overseen by government health departments.